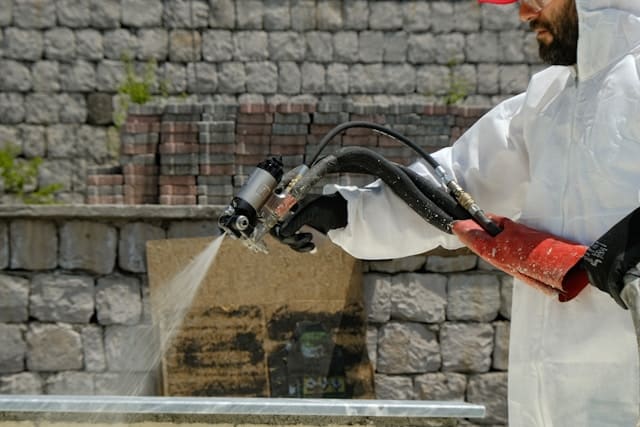
Among the many materials available, polyurea is noted for its durability and is most often associated with its waterproofing capacity. As a coating material, there is no other substance that offers such refined work, making polyurea incredibly widely used. Such characteristics also mean that polyurea is incredibly reliable for both overseas and outside use.
Even though polyurea is widely used worldwide, the technology has a few drawbacks, which must be weighed against the benefits. Understanding both the strengths of polyurea as a coating system is necessary.
Keep reading this guide; we carefully examine this polyurea coating industries flowchart, which is quite complex.
Table of Contents
ToggleUses of Polyurea Coating Industries Flowchart
Despite not being directly involved in the curing process, coating applications should be controlled using optimal environmental conditions to avoid failure. The climatic conditions present on the designed parts during pretreatment and the coating process are a large factor that will affect the long-term performance of polyurea coatings on concrete and steel structures. Using portable electronic devices, contractors, inspectors, and owners can now measure and log the environmental factors relevant to painting.
Advantages and Properties of Polyurea
The following are some advantages of Polyurea waterproofing materials over others:
- Fast drying time: Unlike other materials, Polyurea can cure within seconds. Its rapid setting makes surfaces safe, and you can reuse them immediately.
- Great strength: Polyurea is an excellent option for waterproofing structures likely to endure harsh conditions or heavy use due to its great structural strength.
- Resistant to chemicals: Polyurea coatings can withstand industrial-strength chemicals and compounds, making them ideal for use on surfaces that require waterproofing inside factories.
- Versatile application: You can use Polyurea on a variety of surfaces, including smooth and rough surfaces, allowing it to be applied while working on fences, roofs, pipelines, and tanks.
- Multi-functional: It can use for waterproofing, coating, insulation, and various types of repair work.
- Cracking resistance: Due to its capacity to elongate and shift with the substrate, Polyurea has great cracking resistance.
- Resistant to temperature: Polyurea can withstand extreme temperatures while remaining flexible and endure a wide range of temperatures.
Environmental Considerations of Polyurea Coating
Different demonstrations of polyurea coating systems have included spraying the coating over water and ice, which has no effect on the components’ reactivity. Such conditions may appear stunning from a technological standpoint, but such things will probably never be encountered in application. Specifically, SSPC-PA 14 prohibits the application of a polyurea coating on frosted or ice-covered surfaces.
It is correct that the ambient and substrate temperatures might have minor effects on the reaction and cure of a polyurea system. Still, too much wetness or coldness of either the substrate or the surface to be coated might have detrimental effects on the strength of the adhesion. The SSP-PA 14 also requires that the substrate temperature be greater than the dew point. Thus, you should follow industry-standard practices to correctly apply a polyurea coating system.
To minimize the coatings’ failure probability, both the surface and the coating application, make sure to consider the ideal environmental conditions. Factors that impact the condition of the polyurea coatings on steel or concrete in the long term are mixed. They include the climatic conditions present during pre-treatment and coating application. Coating contractors, inspectors, and owners can now record and measure relevant environmental conditions using portable electronic devices.
Measuring Coating Thickness
Measurement of coating thickness ensures adequate protective coverage while managing costs. Commercial contracts usually require a third-party inspection after the work. Because polyurea coatings and linings are common in containment systems, maintaining the proper thickness is crucial.
You can measure coating thickness through a destructive test for metals like concrete or steel. However, cutting a thinner polyurea coating cleanly to gain an accurate measurement can be difficult because it has elastic qualities. This poses a disadvantage as well because repair work should be done beforehand, which makes it unable to be used for a while.
Repairing the coating afterward is not required, which saves time and money for both the contractor and the inspector, making it easier for the builder. Methods not requiring destruction include gages that use magnetic and eddy current principles for metal substrates and ultrasonic gages for concrete and other non-metals.
Measuring the thickness of polyurea on metallic substrates without damage can be easy as long as the instrument’s range is within the estimated thickness. Since polyurea coatings gain the expected thickness by having multiple layers on top of each other, tracking the individual layer thicknesses will be necessary.
Final Words
The polyurea coating industry flowchart presents an infinite number of advantages and disadvantages of its implementation. Polyurea possesses advantageous characteristics such as water repulsion, enhanced structural integrity, and excellent extensibility that greatly surpass those of competing products. The ability of polyurea roof coating systems to function effectively for 15 to 25 years with several potential renewals of their lifespan makes these systems very desirable.